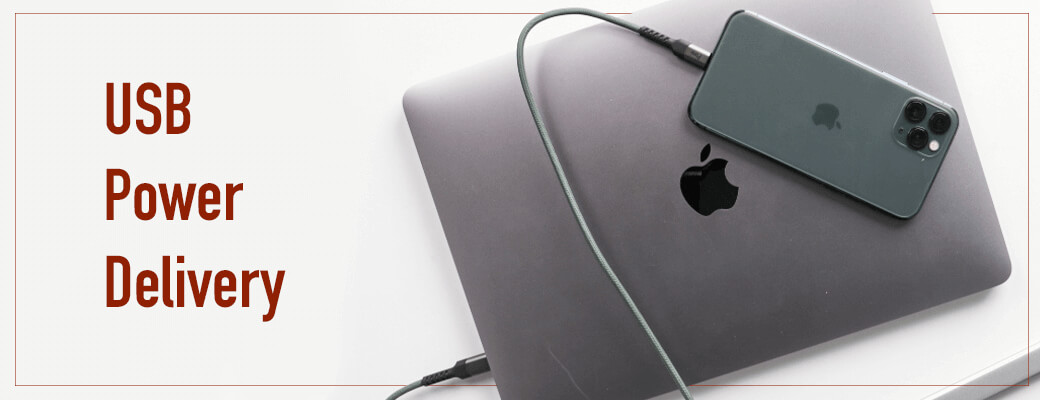
Carrying a portable electronic device has become so common, and so has the need to ensure that the device doesn’t run out of battery at any time. Our social and professional lives have become extremely dependent on the fully charged and perfectly working electronic devices. Therefore, it has become essential to find a way to make things easier for us when it comes to power charging our devices. We were looking for a new way to recharge, and that is where USB power delivery came to the picture.
This has been seen as a major breakthrough in the electronics industry. It enables fast charging and is flexible up to 100W power capacity, which means that it can support charging devices from a small smartwatch to a substantial power-consuming laptop/ computer. It uses the same port for charging, like that of the one used for data transmissions.
The USB Power Delivery (PD) works effortlessly. Firstly, a single USB- C cable is used to connect two devices that are PD enabled. Secondly, both the devices are checked for compatibility; that is, it is analyzed how much power one device can transfer and how much the other can draw from it. This is commonly referred to as a handshake between the devices. Thus, consequently, when both the devices can agree to a common power range, the power delivery between those devices takes place in that agreed capacity. For some, the idea of connecting a charger with 100W capacity, which is designed for laptops, to a smartphone that has a battery capacity of around 2500 mAh, could sound scary. But, not to worry, the USB PD transmits current only at a range that is compatible with the connected devices. The important point to be noted is – as the acceptable range of current charges and the speed at which the device is charged varies directly, so does time taken to get charged, varies inversely.
How did the USB PD originate?
Traditionally, Universal Serial Bus, or USB, acted as an external bus device for high-speed data communication. Then, gradually, there was a need to improve the speed of data communication. As the digital world has always been a fast-growing ecosystem, especially in the 21st century, there was a developing need to have a device that can assist in faster data transfers. There wasn’t, at first, a need to enable power delivery feature in the USB, just so because the focus on that device was on speedy data transmission. But later, as attempts were made to innovate USB that can transmit power, the modern-day USB power deliveries were gradually born. The prototype came about in 2010 when a device was specifically invented and launched to include the power delivery feature. Charging Downstream Port (CDP) mode was introduced in certain USB cables that enabled the flow of current charges at a higher rate, thus making it a PD. This slowly evolved to an extent where every USB cable nowadays comes with the power delivery feature.
The Apple corporation was the first to introduce USB PD charging, in 2015, when they launched their iPad Pro. Later, in 2016, when they launched MacBook Pro, the company enabled USB PD charging for their smartphones, as well, starting from the iPhone 8 variant. Later in 2019, Apple released an 18W USB- C power adapter that came along with their iPhone 11 Pro.
What makes the USB PD different from the usual USB cables?
Let us look at some of the key features of a USB PD. One, the USB PD can handle up to 100W power, which means the charging speed has now been made faster. Secondly, the compatibility has widened; that is, the USB PD can be used in almost all devices. USB PD also takes care of the equipment in a way that it doesn’t allow the device to handle excess power; thus, saving the device from getting overheated.
Are your devices PD enabled?
Many variants of the iPhone and Google Pixel have a USB PD enabled charging feature. Let us make a quick analysis among the several variants and how much time it takes to charge the battery up to 50% to have a clear picture of how the USB PD charging performs. When iPhone X, iPhone 8, iPhone 8 Plus are charged through a lightning to USB- C cable, it takes 30 minutes for the device to be charged up to 50%. Meanwhile, for the iPad Pro, it takes 60 minutes for half battery charge. The two variants of Google Pixel, namely Pixel 2 and Pixel 2XL, when charged through USB- C to USB- C cable, take 37 minutes for half battery charge. However, the calculation of time is also subject to environmental factors and could vary slightly based on those factors under different circumstances.
How much current flows through the various USB- C cables?
USB- C cables are compatible with various modes and carry varied ranges of power. When we discuss a USB PD through a USB- C cable, it can handle current up to 5A, and the voltage varies up to 20V. Also, there are two types of USB- C type ports, with 5V voltage capacity- the 1.5A variant and the 3.0A variant, to handle different power supplies and requirements. Through a QC 4.0, which is a PD compatible, and QC 3.0, the power capacity is up to 4.6A, and the voltage can vary up to 20V.
Is the USB PD charger good enough for iPhone 11 and iPad?
When it comes to iPhone 11, the device supports USB PD fast charging function, and, by default, it comes with a 5W charger. The charging process is very stable through this charger. It starts at 5W, which lasts for 2 hours and 44 minutes, then the voltage becomes constant, and then the power begins to reduce, it drops to below 0.1W from 3 hours and 45 minutes until fully charged. a 5W charger can only charge 16% in 30 minutes, 32% in 1 hour, and takes 3 hours and 45 minutes for a full battery, which is very slow. Luckily, this device supports USB 18W PD fast charger, and you can now charge the full battery by 2 hours and 16 minutes. It can charge 53% in 30 minutes, 80% in 1 hour, and it takes only 2 hours and 16 minutes for 100% battery power. The device also supports a 30W PD charger, where it does a similar job of charging the full battery in 2 hours and 16 minutes. The difference is that it can charge 55% in 30 minutes, 84% in 1 hour, and for a full battery, it takes the same 2 hours and 16 minutes.
iPad Pro, on the other hand, is charged with an 18W USB- C PD charger, which is, by default, available with the device. This consumes power between 17W and 18W, and lasts for 1 hour and 42 minutes qt this range and then gradually drops. It takes 2 hours and 53 minutes to get fully charged. As compared to the earlier version of the iPad, which uses a 12W USB PD charger and takes 5 hours and 32 minutes, this stands to be much efficient.
Is that enough power to charge your device?
The things you need to charge your device are simple- a functioning wall charger and the right USB cable. While choosing the right USB car for your device, it is imperative to understand how much power the device needs to get charged. Smartwatches and wireless headphones need cable that has a minimum watt output of 5W, while a power bank needs as high as 18W. Smartphones require an output band between 18W and 27W, and tablets consume anywhere between 18W and 30W. The heaviest device, when it comes to power consumption, is without a doubt, a laptop, which requires power output between 29W to 100W from the USB cable.
How safe is it to use the USB PD chargers?
The first and foremost safety aspect is that USB PD charges eliminate the need to use an AC adapter and provide one with a simpler wiring structure and hence is clutter-free. In a way to manage devices with extensively ranging power capacities, the USB PD 3.0 has a feature that requires connected devices to identify themselves. The USB PD is also required to pass a USB- IF certification test in order to be used in the system; else, the power flow is restricted to 2.5W by the system itself.
What could we expect to see in the future for PD cable?
A lot of devices/ equipment that we use regularly require cables that can withstand high power sources. The monitors, hard disk drives, printers, for example, require high power flows, which cannot be managed by the existing USB. So, efforts have been taken to come up with USB PD cables that can allow maximum power capacity to charge these devices/ equipment.
While the data transmission is possible in both ways, upwards and downwards through the device, all these days, power flow has been happening only in one direction. The devices have been receiving current charge through direct power sources and stores them to utilize their power requirements. But, in the future, we can expect to see USB PD cables that can transmit power from one device to another, without the need to access a power source directly.
The usage of USB PD could also be extended to cooking appliances for the kitchen and the benchtop equipment. This is due to the fact that USB PD eliminates the need to use an AC adapter and has thus, opened up the possibilities for operating a large variety of devices/ peripherals.
In conclusion, this USB PD charging is all together, a revolution in the field of technology. The whole activity of power delivery has become more comfortable, accessible, and convenient, and now that the devices can share power through a simple current, transmission cables are bringing about a lot of market scope and are available at Pivoi. The future is all going to be a place where power can be shared without any restrictions and limitations!